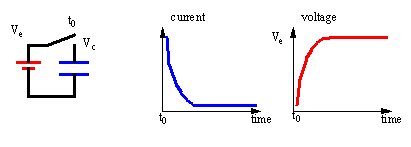
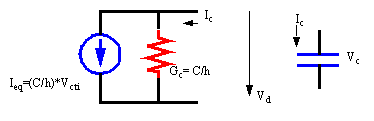The capacitors and inductors have the I-V characteristics
that change with the applied voltage, current and time. The I-V characteristic
is nonlinear and is a function of time.
To illustrate the I-V characteristics of a capacitor
we would need a three-dimensional diagram including both the time-current
and time-voltage graphs.
However, like the linear and nonlinear components, the
capacitor and inductor must be stored in the system equations.
During transient analysis, the solution points are discrete
moments in time. At each timepoint, the numeric integration routines determine
linear I-V relationship for capacitors and inductors. For a capacitor this
linear relationship is given (at each timepoint) by:
Charge-storage elements may be represented with simplified
linear equivalent models calculated in each timepoint.
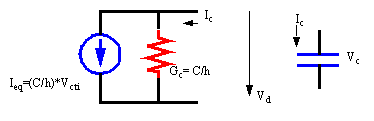
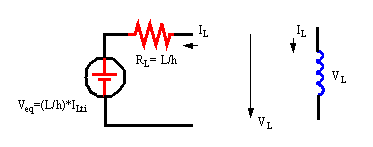
The conductance and current source value for capacitors,
and resistance and voltage source values are recalculated at each new simulation
timepoint by numeric integration algoritms. Once determined they are stored
into the corresponding system matrices.