| nature | effort - across | flot - through |
| électrique | tension | courant |
| mécanique | vélocité | force |
| thermique | temperature | échange thermique |
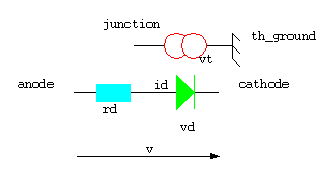
L'exemple suivant est un modèle électrique-thermique
d'une diode ; il nécessite l'utilisation de deux domaines : domaine
éléctrique et domaine thermique
|
package
my_disciplines is
subtype
volt is real tolerance
"voltage";
subtype
temp is real tolerance
"temperature";
subtype
curr is real tolerance
"current";
subtype
heatflow is real tolerance
"heatflow";
nature
electrical is volt across
curr through;
nature
thermal is temp across
heatflow through;
alias
el_ground is electrical'reference;
alias
th_ground is thermal'reference;
end package
my_disciplines;
|
où:

|
use
work.my_disciplines.all
use
IEEE.math_real.all;
entity
my_diode is
generic(is0:
real:= 1.0e-13; rd: real:= 1.0);
port(terminal
anode,cathode: electrical; terminal junction:
thermal);
end
my_diode;
architecture
simple of my_diode is
quantity
vd across id through
anode to cathode;
quantity
vt: voltage;
quantity
temp across power through
ground_th to junction;
constant
volt_equivalent: voltage:11,600.0;
begin
id == is0*(exp((vd -rd*id)/vt) -
1);
vt == temp/volt_equivalent;
power == v * id; -- thermal power
end
simple;
|